Chemical Education Journal (CEJ),
Vol. 13, No. 15 /Registration No. 13-15 /Received july 19, 2009.
URL = http://chem.sci.utsunomiya-u.ac.jp/cejrnlE.html
Appendix
The way of finding numbers in Eqs. (1) - (4) on the basis of
the transformation matrices, the symbols and indices which determine
the type of symmetry:
Type E1u
There are two numbers on the main diagonal of matrices (6); the first one refers to the result of the operation in the first group of hexagons and the other to that in the second. These numbers are the same as in Eq. (1).
The numerical assignments for the remaining degenerate types of symmetry (Eqs.(2 - 4)) are derived on the basis of E1u.
Type E1g
The way of looking for the numbers corresponding to this type of symmetry (Eq. 2) is the same as for E1u except for those transformations which cause the front - back alteration (i, 2S3, 2S6, sh), where the sign change is needed.
Type E2g
This type of symmetry has also the same numbers (Eq. 3) as for E1u, or the numerical results of the operations E, 2C3, 3C2', 3C2'', 2S3, 2S6, sh, 3sd, 3sv are the same for the two types (E1u, E2g), except for i, 2C6, C2, 2S6. For inversion (i) we have index g which means symmetricity with respect to the centre of symmetry, or the inversion matrix has the form:
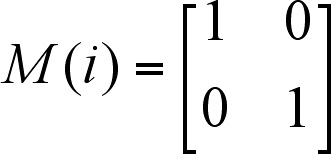
In other words, there are the opposite numbers on the main diagonal
of the E2g inverse matrix to those
of the E1u inverse
matrix. Besides, the type E2g has
index 2 meaning antisymmetricity or the change of the number's
sign at the rotations 2C6, C2,
2S6 (see II.A.(iv)) with regard to those
for E1u.
Type E2u
The way of looking for the numbers corresponding to this type of symmetry (Eq. 4) is the same as for E1g except for (i, 2S3, 2S6, sh), where the sign change is needed. The procedures of inversion of the figures corresponding to E2u and E1g are different because indices "g" and "u" have slightly different meaning for the two types (see II. A. (iii)). On the other hand, the transformations (2S3, 2S6, sh) cause the change of the figure's sign (the figure (figures) transformed through these operations have the opposite signs on both sides of the plane in which the figure is located), and thereby we observe the change of the number's sign with regard to the same operations for E1g.